
Hybrid Clouds vs. Public Clouds: Why Private Infrastructure Is Gaining Ground
August 20, 2024
Global Backbone Becomes a Source of Attacks
September 6, 2025Introduction
Phishing attacks are evolving, and cybercriminals are becoming increasingly creative in how they disguise their malicious intentions. One of the most dangerous trends today involves redirect-based phishing attacks, where attackers cloak harmful URLs behind legitimate-looking domains. This tactic not only deceives users but also bypasses many basic security checks.
At Encryptia Cloud, we recently documented two real-world attempts of this kind, targeting our support@encryptia.cloud mailbox.
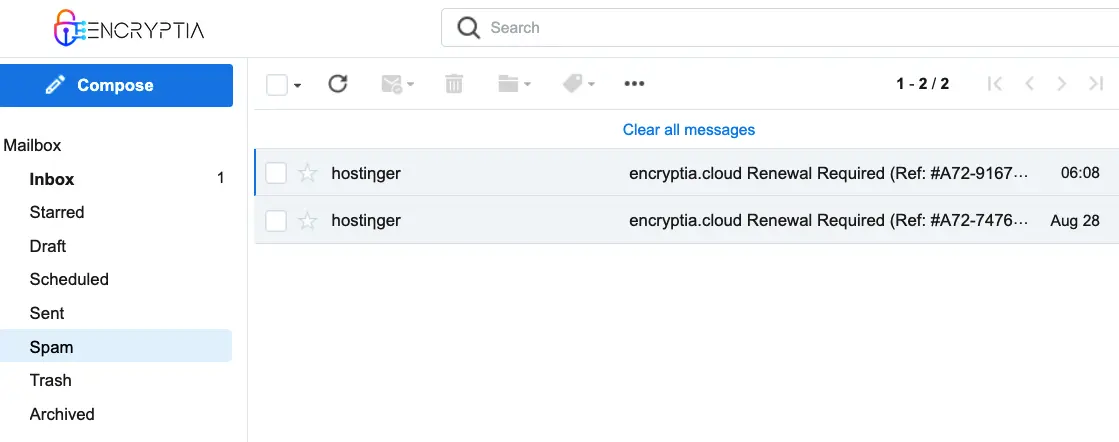
Case Study: Two Attempts Against ENCRYPTIA Cloud Support
In August 2025, our MailPlus secure email server detected and flagged two suspicious emails delivered to the support@encryptia.cloud inbox. Both were immediately quarantined as spam after being identified as malicious.
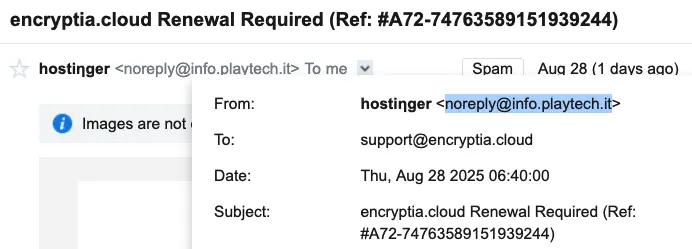
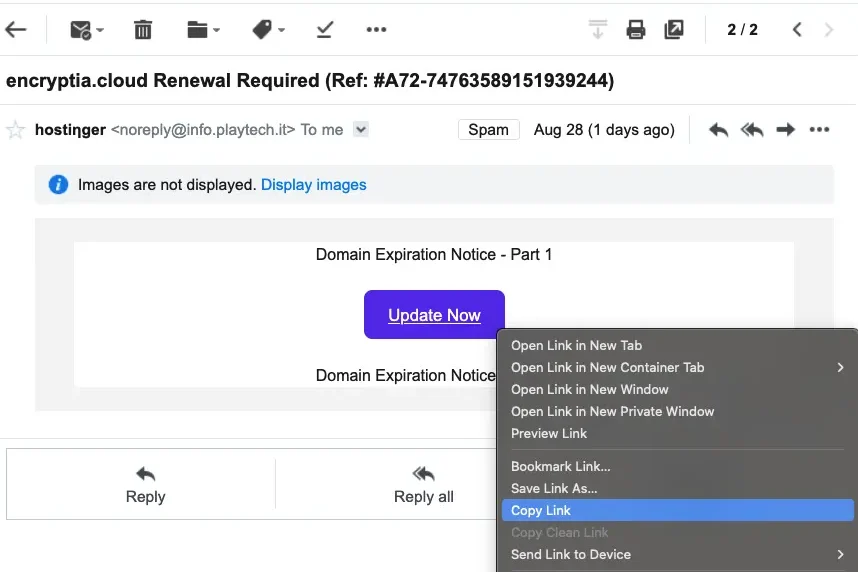
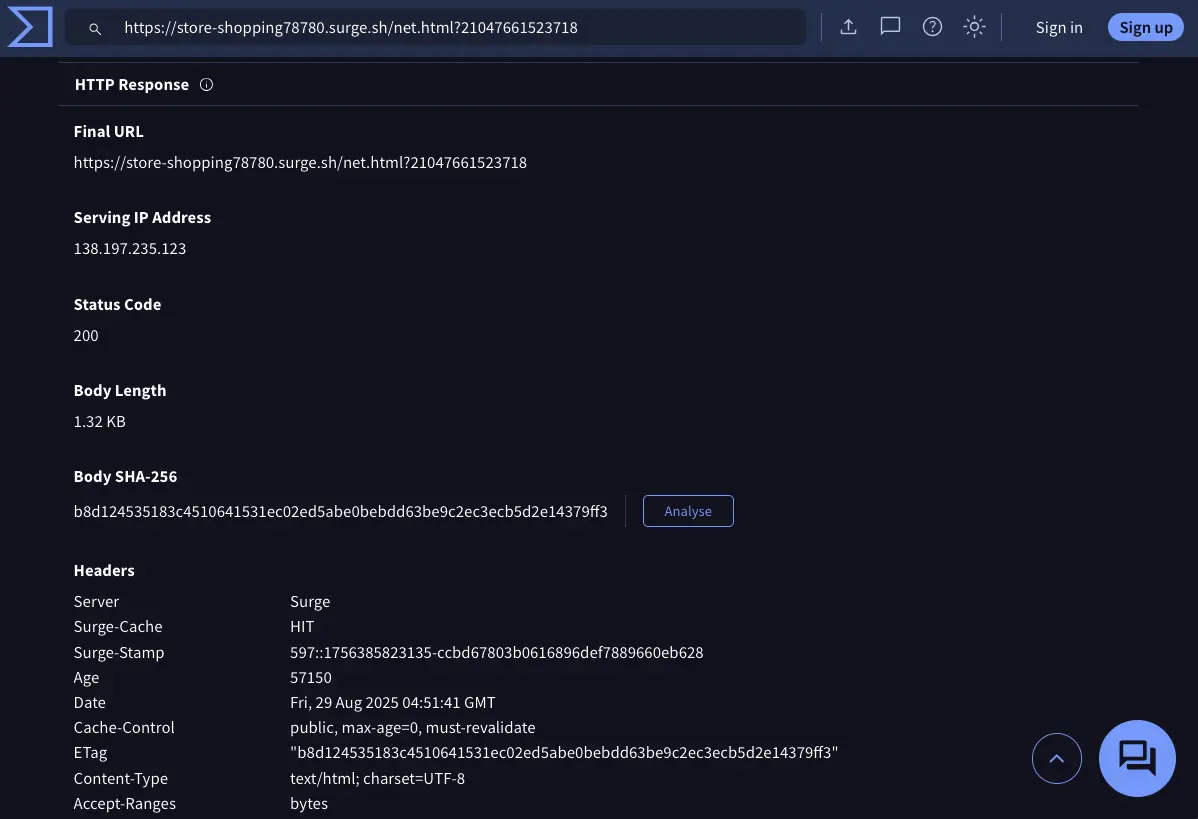
The attackers attempted to lure us with links that appeared legitimate at first glance but, upon closer inspection, were part of a redirect-based phishing campaign. The URLs used href.li redirection and ultimately led to domains hosted on codeanyapp.com, completely unrelated to the brands they impersonated.
To strengthen the deception, the phishing emails were carefully styled to mimic Hostinger’s official communication format, exploiting the brand’s reputation as part of a social engineering strategy. By doing so, attackers tried to make their messages appear authentic and trustworthy, increasing the chance that the recipient would click the malicious link.
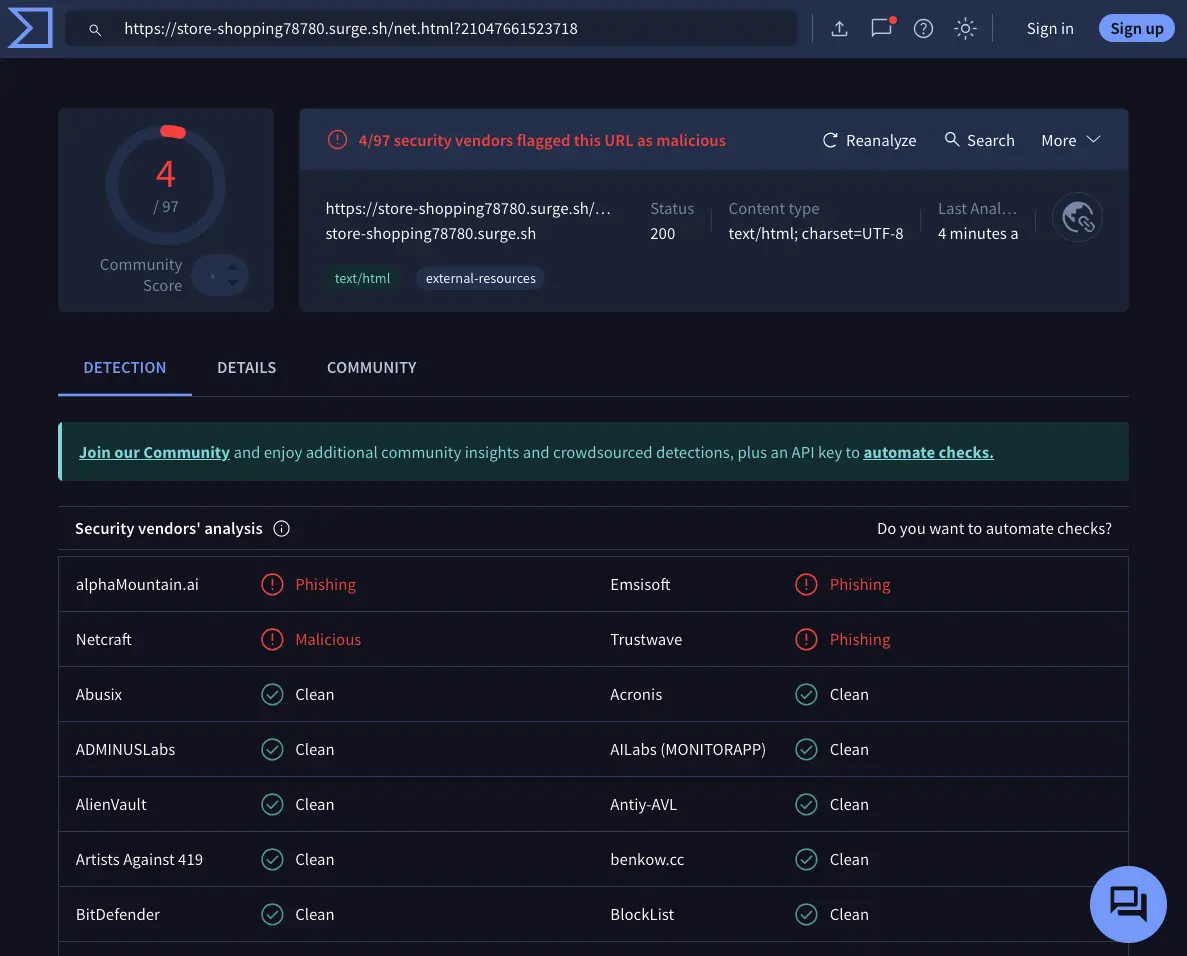
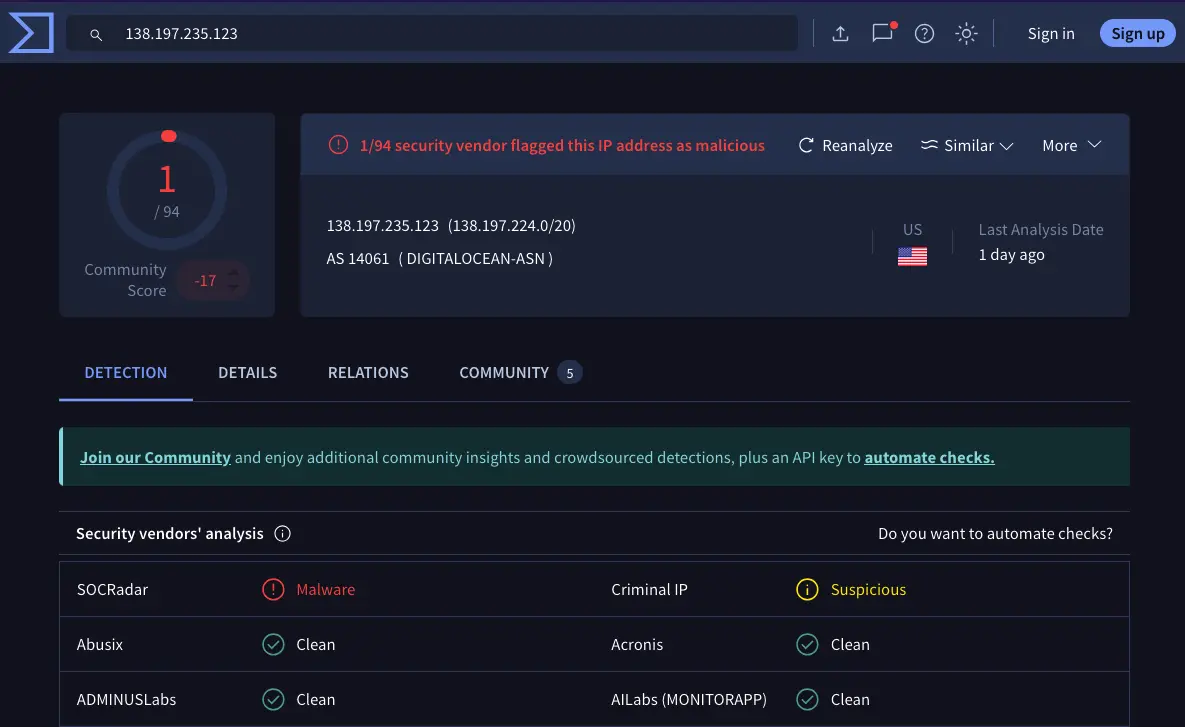
A VirusTotal scan confirmed the risk: one vendor flagged the links as malicious, another as suspicious, and the URLs loaded multiple external trackers, iframes, and resources. The fake pages even mimicked Yahoo Japan’s branding and used misleading metadata to appear authentic.
How Redirect-Based Attacks Work
Redirect phishing attacks exploit user trust by chaining multiple redirects before delivering the victim to a malicious site. The process looks like this:
-
The user receives what looks like a legitimate email.
-
The email contains a link that resembles a trusted brand, such as Yahoo or Hostinger.
-
The link secretly routes through a redirect service like href.li.
-
The final landing page is a malicious domain (e.g., codeanyapp.com) that imitates the trusted brand.
In the case of the two ENCRYPTIA Cloud incidents, the phishing emails were styled to look like Hostinger customer communications, a deliberate social engineering tactic. By copying Hostinger’s branding, attackers hoped to gain trust and trick support staff into clicking the link.
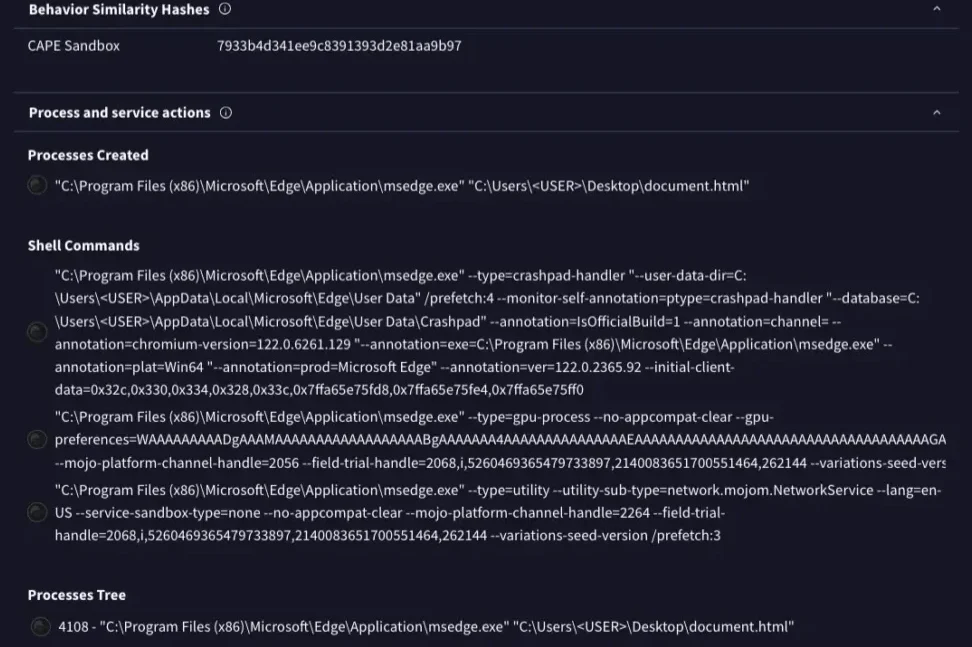
Once on the malicious page, users are exposed to credential theft, injected malware, and data harvesting via hidden iframes and trackers.
Why These Attacks Are Hard to Detect
-
Visual deception: Links appear to come from well-known companies.
-
Redirect masking: Services like href.li make it difficult to see the real destination.
-
Brand impersonation: Attackers duplicate logos, colors, and design elements (Hostinger, Yahoo).
-
Antivirus evasion: Most security engines report the link as “clean” in the early stages, while only a minority flag the threat.
How to Protect Against Redirect Phishing
Defending against redirect-based phishing requires both technical safeguards and user awareness:
-
Use advanced mail filtering: ENCRYPTIA Cloud MailPlus successfully flagged these messages before they reached the inbox.
-
Perform OSINT checks on suspicious links: Tools like VirusTotal provide valuable insight into redirects, trackers, and detection rates.
-
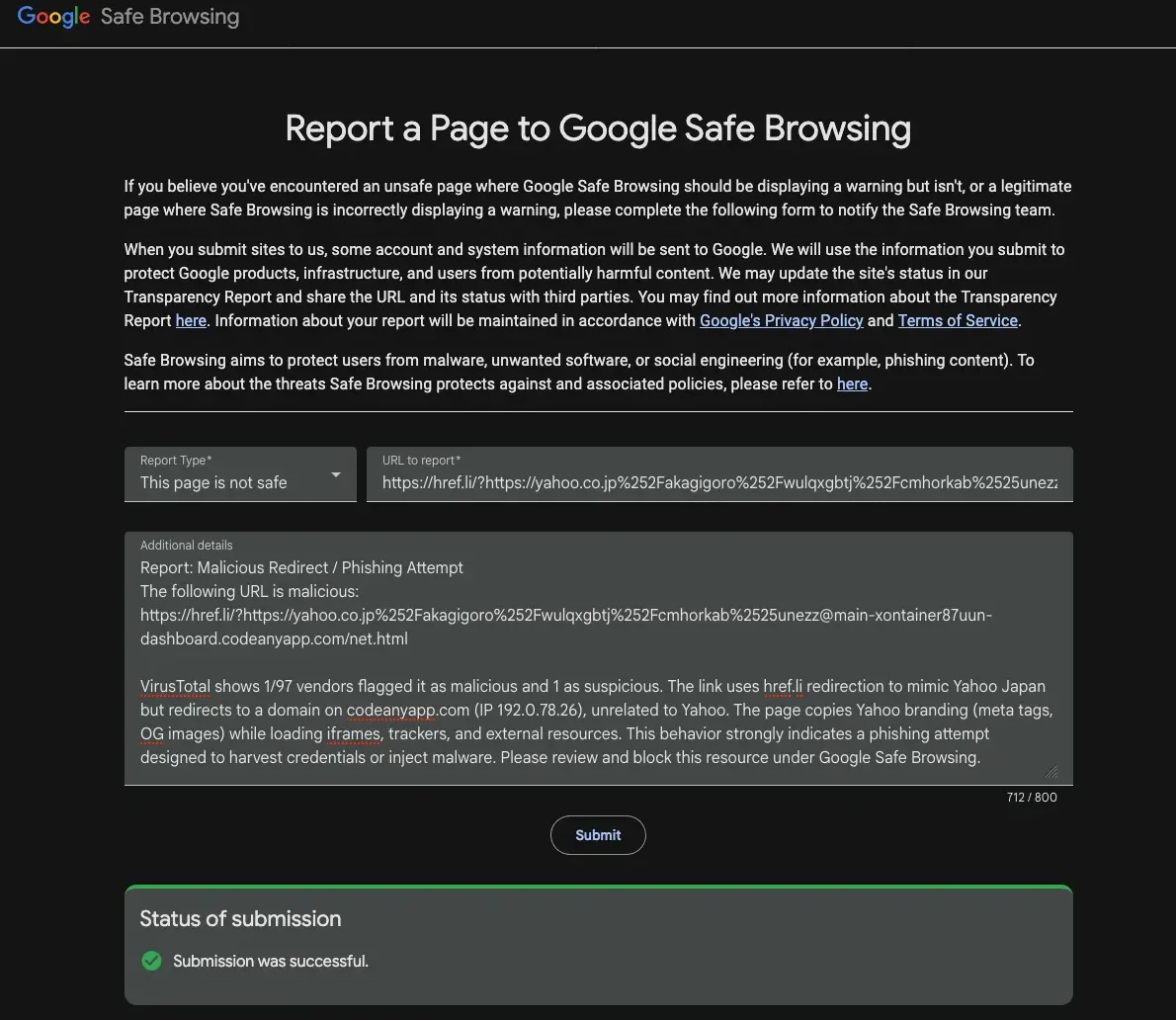
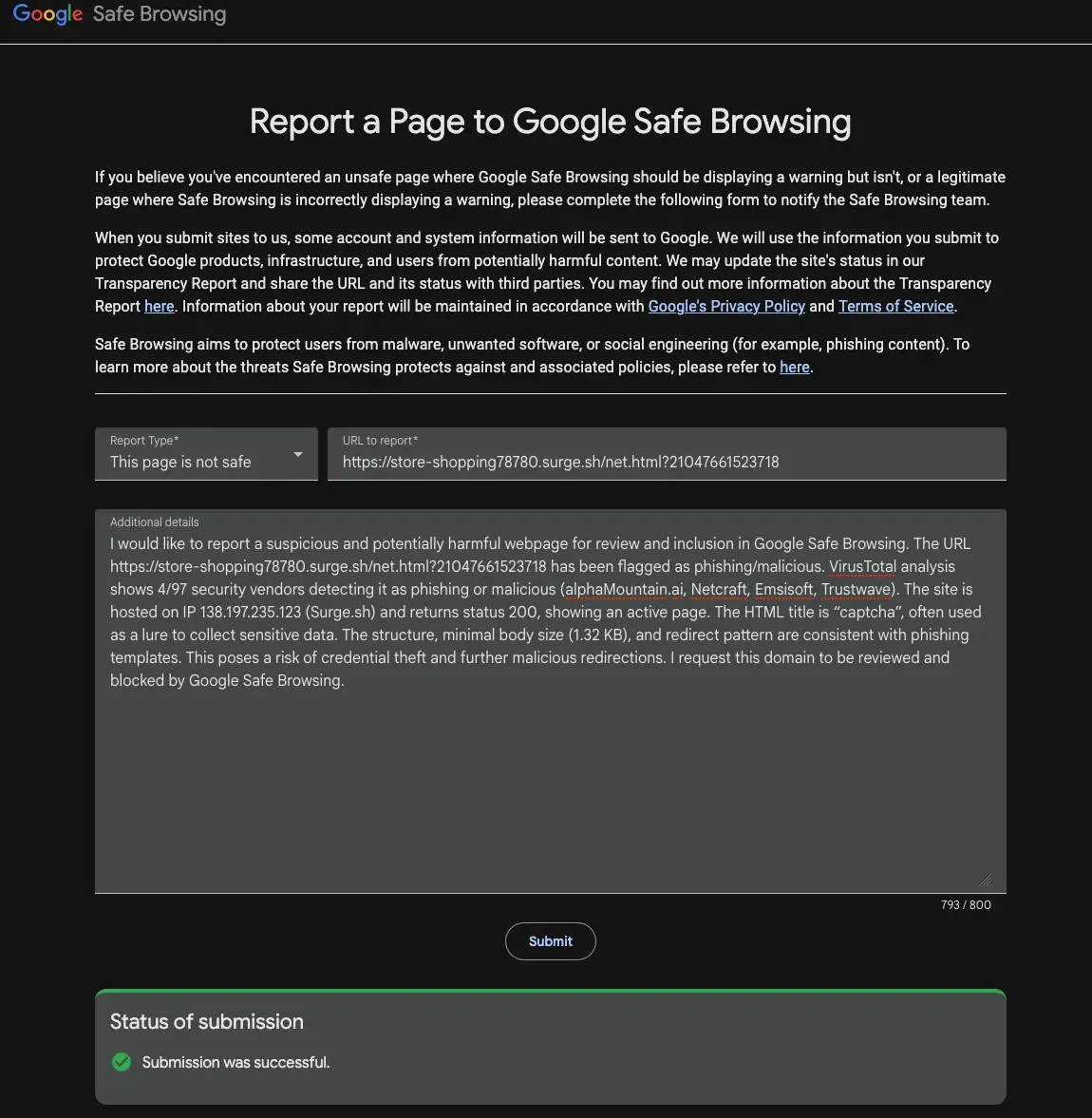
Report malicious URLs: Submitting findings to Google Safe Browsing helps block these threats for millions of users worldwide.
-
Train staff to recognize brand impersonation: Hostinger-style fake emails show how easily trust can be exploited.
-
Adopt a Zero Trust model: Never assume that an email or link is safe just because it appears to come from a known brand.
Conclusion
Phishing through redirect chains is a growing cybersecurity risk, blending technical trickery with social engineering. Our two recent cases demonstrate how attackers exploit brand trust and redirects to try to bypass defenses.
By using OSINT tools like VirusTotal, combining strong email security (MailPlus), and reporting malicious domains to Google Safe Browsing, organizations can both protect themselves and contribute to the wider fight against phishing.
At Encryptia Cloud, our mission is to ensure privacy-first, zero-trust security for all users — because even one malicious link can open the door to a major breach.
Recommendation
If you want to reduce the risk of phishing and exploit-based attacks, start with basic but effective safeguards:
-
Educate your team regularly about suspicious emails and social engineering tactics.
-
Implement multi-factor authentication across all accounts.
-
Use advanced email filtering and endpoint protection tools to catch malicious links and attachments.
-
Conduct simulated phishing tests to measure awareness.
For an extra layer of protection, consider solutions like ENCRYPTIA Cloud, which provide secure data environments and reduce the attack surface for phishing campaigns targeting sensitive information.
ENCRYPTIA Cloud
Los Angeles, CA
Stay Encrypted — Get Updates:
Support
support@encryptia.cloud
Monday - Sunday
06:00 AM - 10:00 PM
Partnerships
partners@encryptia.cloud
Monday - Friday
06:00 AM - 06:00 PM
