Types of Private Cloud
December 15, 2023Today, businesses are moving to cloud for their most critical business applications. It is an excellent way to deliver IT services more quickly and cost-effectively. When looking for a secure cloud option, organizations often choose private clouds. Although businesses were a little reluctant to migrate to private cloud earlier, it quickly emerged as the most secure cloud model.
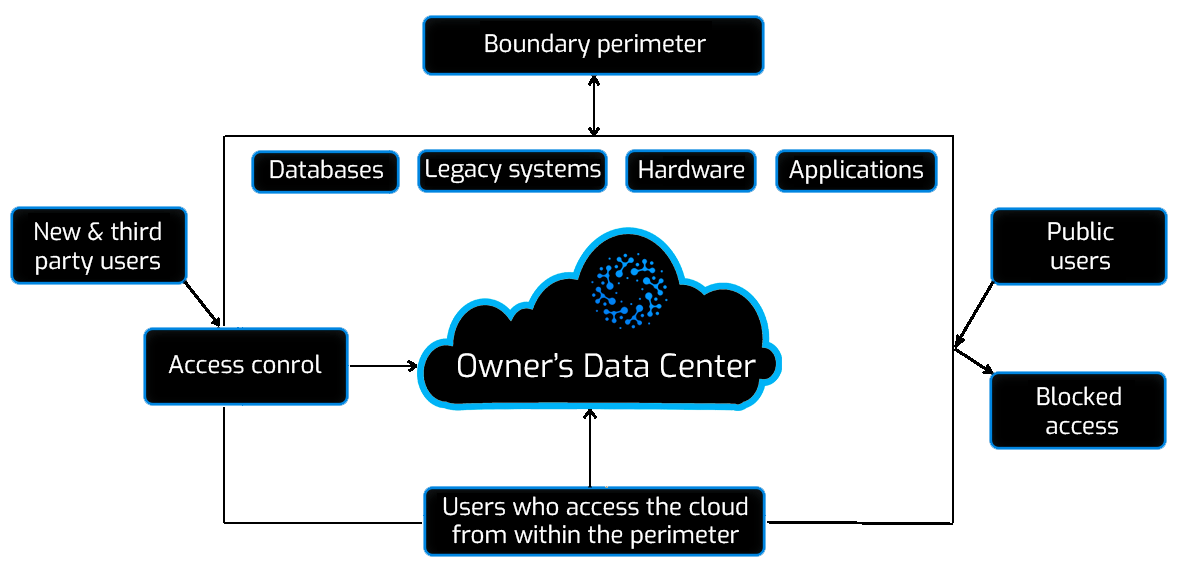
Among types cloud computing, Hosted Private Cloud is the most preferred option for user or organizations due to the additional security it offers. In a private cloud, the cloud computing services and encrypted data storage are hosted privately within a company’s owner data center. This type of cloud is managed by internal resources and is not accessible to those inside or outside the organization.
Advantages and Challenges of Private Cloud
While a private cloud is known for its higher cost, it brings forth a Ultra of benefits.
Let's explore the various advantages offered by a private cloud:
- Robust Security: Private clouds are renowned for providing enhanced security and control. Operating in an isolated environment adds an extra layer of security.
- Enhanced Performance: Dedicated server for each organization. Exclusive accessibility to a single organization minimizes competition for capacity, leading to improved performance. Workload efficiency in a private cloud remains unaffected by resource-intensive tasks from other organizations on a shared server.
- Organizations utilizing a private cloud have the freedom to construct and configure cloud services according to their specific needs. This includes using preferred applications and allocating resources based on business requirements.
Here are some difficulties organizations encounter with private clouds:
- Increased Cost: Private clouds incur higher expenses compared to public and hybrid clouds. This is due to the necessity of investing in private cloud server hardware, maintenance, operating systems, and software licenses.
- Elevated Support Requirements: Establishing a private cloud is more time-consuming and costly than setting up a hybrid or public cloud.
- Limited Scalability: Private clouds lack the scalability of public clouds.
Securing the networking environment, mitigating vulnerabilities, and enforcing end-user behavior are critical, requiring thoughtful execution. While demanding, when done carefully, it is a rewarding endeavor.
Investing in a private cloud mandates overseeing the underlying infrastructure through monitoring, analytics, and troubleshooting. This proactive approach allows enterprises to identify and address issues before they lead to costly downtime resulting from security breaches or mismatched capacity.
Final Considerations
When contemplating the implementation of a private cloud, the options available today are more diverse than ever. Nevertheless, it is crucial to develop a thorough and thoughtful strategy to fully leverage the benefits of a private cloud. The appropriate cloud solution plays a pivotal role in enabling an organization to thrive in a competitive market, fostering business growth, accelerating innovation, and optimizing performance.

